武汉市高校大学生健康素养与生活方式调查
蒋元源 姚颖
华中科技大学同济医学院附属同济医院,武汉 430030
摘要: 目的了解和研究目前高校大学生健康素养与生活方式的现状,为开展营养健康教育提供依据。
方法:按照整群抽样原则,对同济医学院207 名医学生和208 名高校非医学专业学生的健康素养与生活方式进行问卷调查,问卷由调查员统一发放和回收。结果与医学专业大学生相比,非医学专业大学生营养知识得分较低,且男女差
异显著;非医学专业大学生的生活习惯相对不规律,医学专业学生生活习惯也有待进一步提高。结论应采取多种形式对大学生饮食、行为进行正确引导,使之养成科学、合理的生活方式,从而改善高校大学生整体营养与健康状况。
关键词: 大学生; 健康素养; 生活方式
中图分类号: R193 文献标识码: A 文章编号: 1006-2483(2011)03-0031-03
Investigation on health literacy and life style of college students in Wuhan
JIANG Yuan-yuan,YAO Ying
Tong ji Hospital,Tong ji Medical College of Huazhong University of Scienceand Technology,Wuhan,Hubei 430030,ChinaCorresponding anthor: YAO Ying,Email: yaoyingkk@126.com
Abstract:ObjectiveThis study aimed to explore the health literacy and life style of college students in Wuhan,andprovide basis for nutritional health education.MethodsA total of 207 Tongji Medical College students and 208 non-medical college students were recruited as the participants of the study by clusterrandom sampling. The survey includedtheir health literacy and life style. The investigators were in full participation to provide help during the completion of thequestionnaires. All the questionnaires were distributed and called back by investigators.
Results:Compared with themedical majors,the score of nutrition knowledge of the non-medical majors was lower,and difference was also noticed ingender. The non-medical students had an irregular living habit,however,the lifestyle of the medical students still needs to befurther improved.Conclusions
It is necessary to take effective measures to properly guide the college students to havescientific and reasonable life style and habit so as to further improve their nutritious and health status.
Key words: College students; Health literacy; Lifestyle
21 世纪,居民的生活水平有了很大程度的提高,膳食营养作为机体的健康支柱,日益受到人们的重视。大学生是国家未来的栋梁 ,身体素质与合理营养密切相关,正确掌握相关营养知识,科学合理的生活方式可使大学生对其他群体起着引导作用。因而了解大学生的营养知识、态度和饮食行为现状具有重要意义〔1,2〕。为此,于 2010 年 8 月对高校大学生进行了一次健康素养与生活方式的调查。
1.对象与方法
1.1调查对象
采用整群随机抽样方法,在同济医学院中随机抽取的在校大学生 207 名,其中男生 99 名,女生 108 名。在武汉其他高校大学生中随机抽取的非医学专业大学生 208 名,其中男生 142 名,女生66 名。
1.2调查方法
参考 2009 中国公民健康素养调查问卷和文献资料〔3 -5〕自行设计调查问卷,由调查员统一发放和回收调查问卷,学生不记名填写。调查内容主要包括 4 部分:一般情况(年龄、性别等),健康状况(共13 个问题),生活习惯(近半年来的饮食习惯及休闲运动爱好等共 28 个问题),营养知识(内容有营养和合理营养的概念,常见疾病及病因等共 30 个问
题)。
1.3评分标准
营养知识每题 1 分,满分 15 分,得分高低分 3个等级,得分 0 ~ 10 分为一般,11 ~ 20 分为良好,21 ~30 分为优秀。
1.4统计分析
调查得到的资料进行统一编码,应用 EpiData3. 1 软件建立数据库,双人录入并核对,使用 SPSS18. 0 for Windows 软件进行统计分析,分析方法有统计描述,差异性检验。
2.结果
2.1一般情况
共发放调查问卷 458 份,收回有效调查问卷415 (男 241 份,女 174 份),有效率为 90. 61%。
2.2营养知识
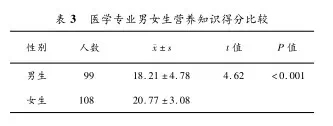
非医学专业学生对营养知识普遍缺乏全面了解,营养知识平均得分为 15. 66,属于良好。男生营养知识得分较低,平均得分 15. 28;女生营养知识得分相对较高,平均得分 16. 48,一般和良好所占的比例比男生低,优秀所占比例比男生高。医学专业学生对营养知识了解情况较好,营养知识平均得分为19. 55,属于良好,女生营养知识得分同样较男生高。医学生得分优秀和良好的比例为 95. 6%,比非医学生 89. 4%高,且医学生优秀所占的比例比非医学生高(表 1)。经差异性检验分析,女生得分较男生高,二者差异具有显著性意义(P < 0. 05)(表 2和表 3)。